A guide to pregnancy monitoring

A guide to pregnancy monitoring week by week - accents
The foundation of this guide are two main theses:
- First, the precise pregnancy monitoring from a qualified specialist with all the necessary modern ultrasound equipment and high-quality laboratory is a crucial factor in the safe development of every pregnancy, and the delivery of every healthy baby.
- Second, the modern tendencies and the European model mother and fetal health care required shared care for the mother and the baby in a partnership between an Ob/Gyn and a specialist in fetal medicine.
A guide to pregnancy monitoring week by week
Below you can see the standard model in the monitoring of every normally developing pregnancy in the Center for prenatal and fetal medicine in Dr. Shterev Hospital, including all the required tests and examinations.
The pregnancy is separated in 40 weeks, called gestational weeks. The beginning of the week is the same as the first day of the last menstrual cycle before the conceiving. In these 40 weeks the monitoring of every woman is unique, according to her general health condition, age, and pregnancy development. These are the factors that determine the frequency between the examinations, the specific tests that have to be performed, and if necessary, the pregnant woman may receive advice for additional consultations with a specialist from different medical fields.
Pregnancy test (Fourth gestational week)
The first step of the monitoring of every pregnancy is its detection. In the home this happens with a urinary pregnancy test, which can be bought from every pharmacy. For fair result the urinary analysis should be performed approximately 14 days after the conceiving. When the test is positive, it could be repeated in 48 hours for further confirmation. In this time the woman has to inform her Ob/Gyn specialist for the test result and to start taking folic acid (400 micrograms per day) if she has not started yet.
First Ob/Gyn examination (Fifth-Sixth gestational week)
The next step is booking an appointment with Ob/Gyn specialist for outright confirming of the pregnancy. The physician may require a blood pregnancy test, which is advisable if the examination is in a too early stage of the pregnancy and it still cannot be detected with an ultrasound diagnostic.
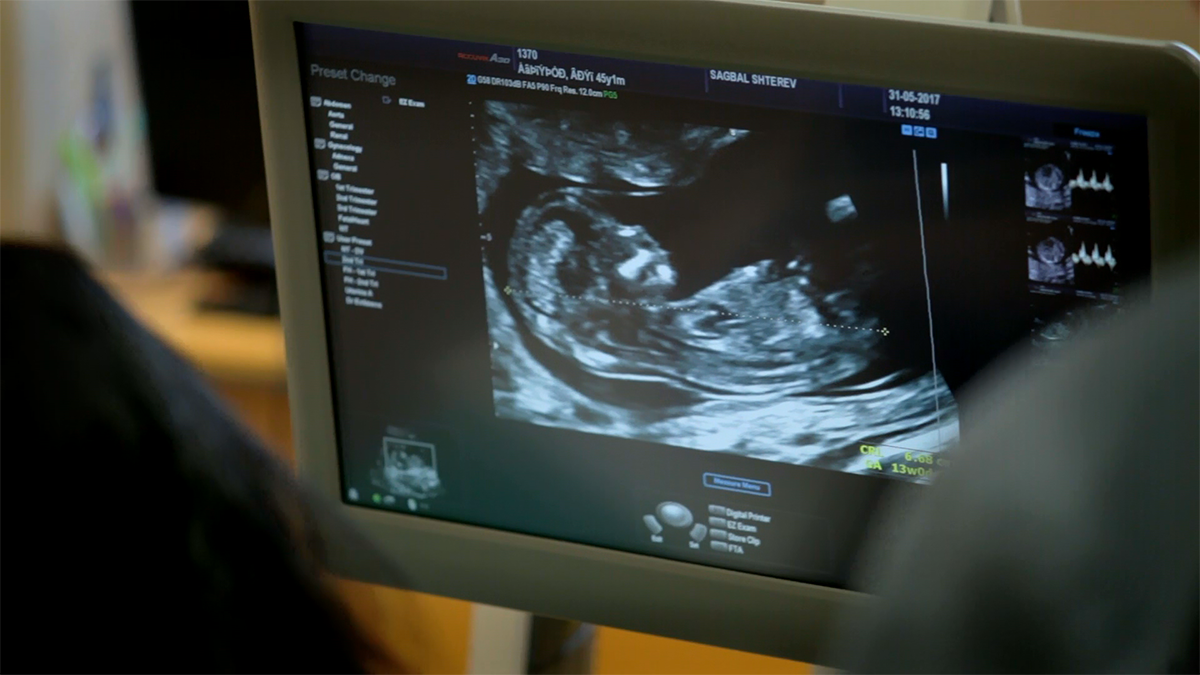
It is recommended to book your first medical appointment at least a week after the delay in the menstrual cycle (fifth gestational week). It is the first time when the pregnancy could be detected with an ultrasound examination. Usually, in this period the ultrasound diagnostic identifies the so-called gestational sac, but the embryo and its heart beating cannot be registered yet.
It is when pregnancy monitoring starts
From now on every appointment with Ob/Gyn specialist (pregnancy monitoring examination) will include ultrasound diagnostic, weight measurement, blood pressure check, metering of the circumference of the abdomen, and control over the healthy development of the baby with the necessary fetal biometry. Besides, the woman will receive advice from the physician about the pregnancy, her and her growing baby’s health. If the patient has some comorbid conditions, her doctor will guide her for additional consultations with another specialist, if this is necessary. If the pregnancy is developing typically, by the fifth month or the 22-26 gestational weeks, the examinations will be monthly.
Second Ob/Gyn examination (seventh-eight gestational weeks)
This second examination with ultrasound diagnostic, which is the start of the actual pregnancy monitoring, usually comes two weeks after the first examination for the detection of the pregnancy. It is longer and includes a conversation about woman’s past and present medical conditions and illnesses, calculation of the pregnancy due date and estimated date of delivery according to the last regular menstrual cycle. The examination also includes a measurement of weight, height and blood pressure. The ultrasound diagnosis is transvaginal, and its purpose is to hear the heart beating of the fetus and to detect its position in the uterus. This part of the examination proves to the healthy development of the pregnancy in the womb. With this medical appointment begins the monthly monitoring of the condition of the pregnant woman and the development of her growing baby
On this and every next monthly examination the Ob/Gyn specialist may require regular lab tests, like complete blood count (CBC), urine, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
Additional examinations
During the pregnancy, the physician may require immunohematology testing of the woman, if she has not performed it yet, for determining her blood type and rhesus factor. Also, in every moment the doctor may ask for microbiology of vaginal discharge and sterile urine. The first one is mandatory after 36-38 gestational weeks, no matter if it is already done during the pregnancy. If the woman lives with pets, she may need to make a test for toxoplasmosis or other zoonosis diseases.
First examination from fetal medicine specialist - first-trimester screening test (11-13 gestational weeks)
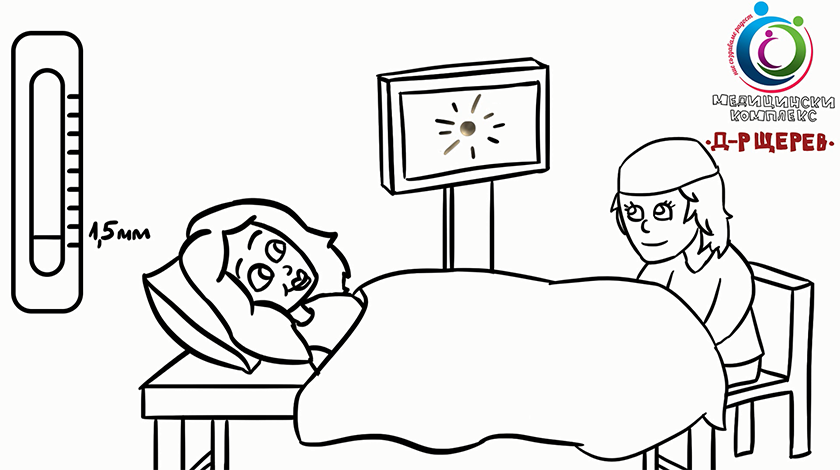
The first-trimester screening test determines the risk for the fetus of Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome), and Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome). The examination includes ultrasound observation of the fetus and measuring the “fluid” behind its neck (nuchal translucency), assessment of the nasal bone, the right ventricular outflow tract and the ductus venosus, which is a small blood vessel in the fetus’ liver. The examination also includes blood testing for two substances produced by the placenta - free beta subunit (free β-hCG) and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A). Particular software combines the results from the ultrasound diagnostic and the blood test and calculates the risk from trisomy 21, 18, 13. The first-trimester screening test can detect abnormalities in 90 to 95% of the cases with one of those trisomies. This examination is recommended for every woman in the specified period of her pregnancy, no matter one or more offspring develop during the gestation. In addition to the information for the trisomies, this test helps the detection of large anatomic abnormalities of the fetus. In high-risk cases for delivering a baby with defects, the patient may choose from additional invasive examinations, like chorion biopsy and amniocentesis, and non-invasive blood tests of the fetal DNA, which held no risk for the pregnancy. This examination between 11 and 13 gestational weeks allows the fetal medicine specialist to provide the woman and her gestation monitoring doctor detailed information from the aneuploidy screening, about structural defects of the growing baby, and for the overall risk for the developing pregnancy.
After the 13th gestational week the Ob/Gyn specialist may require blood sugar test, and additional biochemical indicators testing for coagulation, like prothrombin time, fibrinogen, and PTT (partial thromboplastin time).
From now on every ultrasound examination will measure the primary structures of the fetus and will observe its growth and development (fetal biometry) and if they correspondent to the stage of the gestation. It will evaluate the fetal movements and activity, and the position of the placenta and the umbilical cord.
Third medical appointment with the Ob/Gyn specialist 916-20 gestational weeks)
This appointment includes a transabdominal ultrasound examination, and also all the routine measurements of the pregnant woman and her condition. The patient must complete some standard blood tests like CBC and ESR.
According to the results of the first-trimester screening test and if the Ob/Gyn specialist decide that it is necessary, this stage of the pregnancy is the exact time for performing an amniocentesis.
Second examination from fetal medicine specialist - high-quality ultrasound observation of the fetal morphology (19-23 gestational weeks)
The next recommended ultrasound examination from a specialist in fetal medicine in between 19 and 23 gestational weeks, and it is about the fetal morphology of the baby. The specialist carefully observes the development of the fetus, aiming to exclude every possible structural defect. Through this fetal morphology examination, the doctor and the future parents reassure that the heart, the face, the arms and legs, and all the anatomy of their baby have developed correctly. Besides, the fetal medicine specialist checks the normal functioning of the placenta and makes a prognosis about the risk for preeclampsia or for forming a small for its gestational age fetus. If this is in the forecast, the specialist recommends the best way for the delivery and analyses the long term neurological development of the baby.
Additional examination from a fetal medicine specialist - fetal echocardiography (18-22 gestational weeks)
At the discretion of the gynecologist and after consultation with fetal medicine specialist, the pregnant woman may receive the advice to perform echocardiography between 18 and 22 gestational weeks - a specific ultrasound examination of the baby’s heart. Echocardiography examines the position, size, structure, function, and rhythm of the baby in the woman’s womb. The method uses two-dimensional echocardiography (2D), Doppler for reviewing the blood flow through the heart valves and vessels, and colored doppler for visualization of the blood flow direction. The prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart abnormalities gives a chance for preventing some of the complications, connected with a later postnatal diagnosis. Echocardiography is recommended when:
- The gynecologist detects abnormalities of the fetus’ heart during a routine ultrasound examination
- In cases of heart disease heredity, abnormal heart rhythms, abnormalities of other central systems or organs of the baby
- The pregnant woman has diabetes, fenilcetonuria, etc.
- The woman takes some specific medicines during the pregnancy
- In cases of chromosomal abnormalities, connected with congenital disorders.
The most appropriate time for complete echocardiography is between 18 and 22 gestational weeks.
Fourth appointment with the gynecologist (22-26 gestational weeks)
It is a routine consultation, which includes all the examinations and tests, necessary for the observation of the pregnant woman’s condition and the development of her baby (described above). After the 20th gestational week, every medical appointment includes assessment of the placenta functioning, and the ultrasound diagnosis is with Doppler observation of the blood flow in the baby and uterine blood vessels.
Examinations and tests after the 28th gestational week
In this stage of the gestation the woman continuous with regular ultrasound examinations, monitoring of her health and the development of her baby through recording its biometrical data and fetal growth. All the routine tests described above continue, and if everything with the patient goes normal, there are in total four gynecological examinations as a part of the pregnancy monitoring.
After the 28th gestational week, part of the regular pregnancy monitoring becomes the nonstress test (NST) of the fetal heart rate in every two weeks. The NST or cardiography is performed with equipment called cardiograph or fetal heart monitor. This examination monitors two parameters. The first one is the intrauterine condition of the fetus in dynamic, which is established through the changes of the baby pulse frequencies, and they are printed in a curve on a paper. The cardiograph allows you to track the sound of the fetus heart beating in real time. NST makes it possible to identify specific types of fetal suffering to be able to take proper actions on time. It is essential that the NST diagnostic only rounds out but cannot replace the detailed Ob/Gyn examinations of the pregnant woman from her doctor with ultrasound diagnostic and doppler observation. Another function of NST is tracing the uterine contractions by measuring their strength, duration, and frequency. The results are printed on the same paper beside the baby pulse frequencies curve.
Third appointment with fetal medicine specialist - third-trimester fetal morphology with doppler (30-32 gestational weeks)
This highly specialized examination evaluates the excellent condition of the baby at the end of the gestation. It is performed with Doppler ultrasound diagnostic, which gives information about the blood flow in the different blood vessels of the baby, and also in the umbilical cord and the uterine arteries. During this appointment, the specialist re-evaluates the organs and systems of the baby. This stage of the pregnancy is the time for assessment of the condition of the baby in the womb and for detecting of some complications, which may require increased attention from the specialist who monitors the pregnancy, and from the team responsible for the upcoming delivery.
Examinations and tests after the 36th gestational week
Around the 36th gestation week, the woman has to perform some blood tests, like hepatitis B and C, Hiv (advisable). These tests are also acceptable in the early stages of the pregnancy, but their validity period is up to 6 months, so the usual practice is to perform them in the beginning and at the end of the pregnancy. The early testing is at the discretion of the gynecologist, and at the end of the pregnancy is a mandatory part of the documentary preparation for the upcoming birth.
A mandatory part of the preparation for the delivery between 36 and 38 gestational weeks are these tests: microbiology of vaginal discharge, CBC, blood sugar, creatinine, albumin, total protein, urea, urine (the gynecologist may ask for sterile urine), and coagulation factors - fibrinogen and prothrombin time. 36-38 gestational weeks is the stage of pregnancy for consultation with cardiologist and anesthesiologist, and preparation of the medical questionnaires and informed consents for the future delivery.
After the 36th gestational week, the NST becomes weekly. It is the ending period of the gestation and delivery may occur in every time to the estimated delivery time. In addition to the weekly NSTs, the woman has to pass a detailed gynecological examination and consultation with the Ob/Gyn specialist who has been monitoring the pregnancy up to now. This examination is the time for the final determination of the position of the baby and its lowest part - head, seat or other. The doctor discusses with the woman the delivery, and if there are medical indications for cesarean section, they plan the date for it.
This period is the final of the pregnancy monitoring and the beginning of the expectation for the forthcoming birth.
A guide to pregnancy monitoring week by week - contact us
If you want to be sure about your baby’s health and your pregnancy development, call us on +359 2 920 0901. We will sign you an appointment with one of the best Ob/Gyn and fetal medicine specialists.
Do not forget to ask about our subscription pregnancy monitoring packages! According to our practice, they are the most secure and at the same time cost-effective way of pregnancy monitoring. Besides, you will also get a discount of the delivery price and will have the chance to give birth under the care of the specialist, who has been monitoring your pregnancy and knows you and the development of your little treasure best.
Video: Our fetal medicine specialists
They are the doctors who take care of the tiniest patients in the mommy's belly. They show you the smile, the hands and the feet of your baby even before its birth. We present you our fetal medicine specialist and the Fetal Medicine department of Dr. Shterev Hospital.
Take a few minutes to learn when are performed and what information about the condition of the pregnant woman and her baby give the three highly specialized fetal medicine examinations - first-trimester screening test, fetal morphology, and third-trimester fetal morphology with Doppler examination.
Video: Everything about your pregnancy in Dr. Shterev Hospital
The complex of special precaution, highly qualified medical care and education initiative in Dr. Shterev Hospital help women to pass through their pregnancy tranquil for their health and the development of their babies. They are also very well informed of what to expect, and this is how pregnancy becomes a period of expectation, but even confidence and joy. Watch the video about the exclusive prenatal care in Dr. Shterev Hospital, and learn more about the education initiatives with lectors who are healthcare specialist.
Video: The first trimester of the gestation
We meet you again with the charming Dr. ARTi from Dr. Shterev Hospital, who will introduce you in this video with the changes in woman’s body in the first trimester of the gestations, and with the required examinations and tests in this stage of the pregnancy. More videos about the medical care in Dr. Shterev Hospital are available on our YouTube channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/ShterevHospital
Video: The second trimester of the gestation
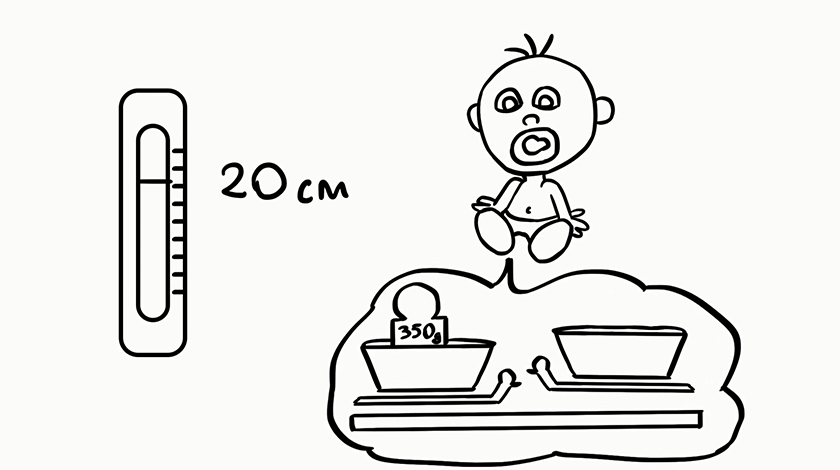
At the beginning of the second trimester the baby has already started to suck its thumb and is actively moving in the mommy's belly. From our video, you will learn about the mandatory and the recommended examinations and tests at this stage of the pregnancy, and how week after week the baby becomes stronger and more prepared for your first meeting. Dr. ARTi will explain to you when the baby starts gaining fat, have pigmentation of the hare, an what is its weight in the 24th gestational week. More videos about the medical care in Dr. Shterev Hospital are available on our YouTube channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/ShterevHospital
Video: The third trimester of the gestation
We meet you again with the charming Dr. ARTi, who will now introduce you to the third trimester of the pregnancy funnily and transparently. Watch our animated video to learn how the baby changes in the last weeks in the mommy’s belly, and what are the essential tests and examinations for the preparation of the woman for the upcoming delivery.
Video: Fetal medicine examinations
We meet you again with the charming Dr. ARTi, who will introduce you to one of the most critical examinations during the pregnancy - those performed by the fetal medicine specialist. Watch our animated video and earn more about the first-trimester screening test, the fetal morphology in the second and in the third trimester of the gestation.
A guide to pregnancy monitoring week by week - resume
The physician who performs fetal morphology or fetal operation must have the certification for them. It is the only way to receive the best medical care for you and your baby.
 Медицински комплекс „Д-р Щерев”
Медицински комплекс „Д-р Щерев”