PGD/PGS - accents
- PGD (Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis) allows early diagnostic of embryo’s genetic diseases of couples who carry DNA disorders or are at risk to transmit such diseases to their children. The method was applied for the first time in 1990.
- PGS (Preimplantation Genetic Screening) allows early diagnostic of aneuploidy (chromosomal anomalies - additional or missing chromosome) in the embryo karyotype. The method was applied for the first time in 1993.
- See below our exclusive video for the techniques which increase IVF success rates.
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis/Screening (PGD/PGS)
What is PGD/PGS?
PGD allows early diagnostic of embryo’s genetic diseases of couples who carry DNA disorders or are at risk to transmit such diseases to their children. The method was applied for the first time in 1990.
PGS for aneuploidy allows early diagnostic of chromosomal aneuploidy (chromosomal anomalies - additional or missing chromosome) in the embryo karyotype. The method was applied for the first time in 1993.
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) helps the detection of various genetic disorders, predisposition to cancer, Alzheimer’s and other diseases before embryo transplantation and pregnancy. After the diagnostic process, only healthy embryos are selected and transfer in woman’s uterus. Thus the risk of miscarriage, medical abortion or delivery to a baby with some genetic disease could be minimized. It is necessary to use assisted reproductive techniques (IVF or ICSI) to apply PGD to oocytes or embryos.
What are the differences between chorionic villus sampling (CVS), amniocentesis and PGD?
The main difference between chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis, on the one hand, and PGD, on the other hand, is that the first two methods detect fetus anomalies after the pregnancy has already occurred. PGD is the earliest diagnostic form with detects embryo anomalies before the occurrence of pregnancy. It helps to avoid a potential pregnancy termination and give a chance for the couples to start a pregnancy knowing that their future child does not carry genetic disorders.
When is PGD advisable?
PGD applies to both infertility patients and those without reproductive problems but with those factors:
• Repetitive miscarriages with detected fetal anomalies
• More than three unsuccessful IVF/ICSI procedures with very good embryos on day 5
• Medical history of a previously born child with chromosomal disorders
• Family medical history for chromosomal structural disorders (i. e. translocations, inversions, etc.)
• Family medical history of X chromosome disorders
• Heritable genetic anomalies
• Predisposition to cancer, Alzheimer’s, etc.
What are the benefits of PGD?
The method helps:
• Giving birth to e healthy child
• Growing a healthy adult with longer life expectancy together better health indicators (especially for cancer and Alzheimer’s predisposition)
• Conceiving and developing a pregnancy without fetal genetic anomalies to women with advanced age, which is considered to be more than 35 years according to the world standards
• Success in IVF for couples with multiple unsuccessful assisted reproduction procedures
• An additional increase in the success rate of ART
• The decrease in the risk of miscarriages and pregnancy loss at both early and late stage
• Reducing the number of multiple pregnancies through the selection and transfer of fewer embryos but with higher implantation potential
• Potential assessment of the entire embryo genome
PGD step by step
Step 1: Preparation
This stage includes the development of a PGD strategy for the preliminary optimization and validation of the PGD protocol before its clinical implementation. Additional genetic examinations of the couple and consultation with a genetic specialist may also be required.
Step 2: Controlled Ovarian Hyperstimulation (COH)
See the stages of an IVF procedure here.
Step 3: Oocytes collection
Step 4: Oocytes fertilization
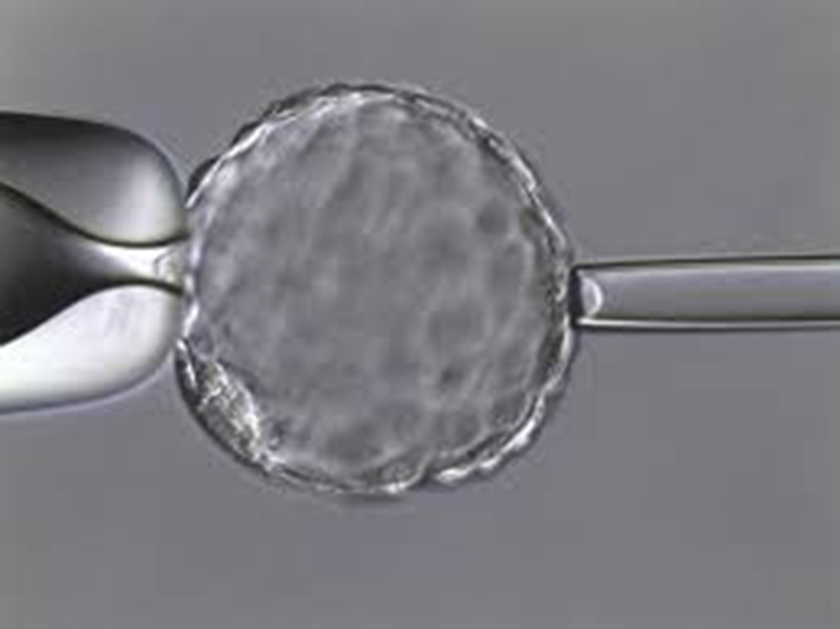
Step 5: Biopsy of an embryo or a polar body
Recent studies show that the diagnostic of the first and second polar body is non-informative. It does not provide information for the genetic of the male gamete, as well as the errors of the chromosomal distribution, which may occur in later development stages of the fertilized oocyte. This method is not applied in the laboratories around the world except for countries in which biopsy of developing embryo is not allowed.
Another possible stage for biopsy is the eight-cell embryo. It is usually the stage on day 3 after the In Vitro Fertilization. This stage does not provide with enough information, because 50-60% of all embryos are mosaic, which means that they contain both healthy and diseased cells. Some of the embryos regenerate from the diseased cells or exclude the healthy ones to day 5. Because of that diagnosis on day 3 can interrupts the embryos self-correction, and by that, may provide a false positive or false negative result from the genetic diagnosis.
The most accurate analysis, which does not interrupt the embryo development, is the blastocyst biopsy on day 5. At this stage, the mosaicism is at its lowest level (about 10%), and the analysis is most reliable. The cells for the analysis are extracted through a hole in the embryo shell (Zona Pellucida), made by a laser. An embryologist aspirates the cells with a micropipette. Cell collection is performed only to expanded blastocysts. These are the embryos with clear development of two parts - one will form the fetus, and the other will become the placenta. The biopsy is performed to a small part of the cells of the future placenta because this way the examination does not interrupt the embryo development.
Fifth-day embryo (blastocyst) biopsy is the common practice in most certified European laboratories, as it is most safe and informative. It is combined with embryos cryopreservation until the results are received and confirmed.
When pregnancy is achieved, the results from day 5 biopsy must be confirmed with additional examinations.
Step 6: Biopsied cells are analyzed for different genetic disorders
Step 7: After embryo transfer, the achieved pregnancy is carefully observed
The results from PDG have to be confirmed with amniocentesis or another form of prenatal fetal diagnosis.
Techniques for increasing the success rate in IVF - contact us
The composers of joy - here you can meet the embryologists and biologists of Dr. Shterev Hospital. Every day they apply the highly specialized techniques which increase the chances for success of the couples with reproductive problems.
Book your appointment with a reproductive specialist via a phone call to +359 2 920 09 01 or via our digital communication channels - website, Viber, Facebook Messenger.
Video: Techniques for increasing the success rate in IVF
Watch our cartoon video, in which brightly and funnily we will introduce you to the high-tech procedures, implemented in Dr. Shterev Hospital. You will learn about the additional techniques and methods, which increase the success in ART. You will also learn when and why we execute them.
Video: The joy we create
Watch the video to learn how the complex names of the different IVF lab techniques transform into the most significant celebration to our patients.
Techniques for increasing the success rate in IVF - resume
For more than 30 years the team of Dr. Shterev Hospital has been helping thousands of women and couples to feel the greatest joy - to hear the laughter of their baby. In the last years, the success rate in couples with different types of infertility has increased significantly. The main reason for this increase is the application of most modern additional techniques, which help in cases where nature cannot succeed.
Additional IVF Techniques
Additional IVF Techniques
назад- EmbryoScope (Time-lapse embryo imaging)
- EmbryoGlue
- Local Endometrial Injury (LEI)
- Growth medium for RIF/RPL
- Intracytoplasmic Morphologically Selected Sperm Injection (IMSI)
- Assisted Hatching
- Co-cultivation of embryos
- Magnetic Activated Cell Sorting (MACS)
- Calcium activation
- Spindle View and Zona Pellucida Analysis
- Endometrial Receptivity Analysis
 Медицински комплекс „Д-р Щерев”
Медицински комплекс „Д-р Щерев”